What Are the Best Relaxation Techniques in Postnatal Yoga?
The postpartum period represents one of life’s most profound transitions, bringing not only the joy of new life but also unprecedented physical recovery demands, sleep disruption, identity shifts, and emotional adjustments. During this vulnerable time, relaxation isn’t merely a luxury but a physiological necessity supporting healing, milk production, emotional regulation, and the energy reserves needed for infant care. Postnatal yoga offers specialized relaxation techniques specifically designed to address the unique needs of new mothers, creating moments of restoration that support both maternal wellbeing and the capacity for present, responsive parenting.
Understanding Postpartum Relaxation Needs
Before exploring specific techniques, understanding the unique aspects of postpartum relaxation provides important context:
The Physiological Imperative for Relaxation
New mothers face distinct physiological challenges:
- Recovery from Birth: Whether vaginal or cesarean, birth requires significant tissue healing
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Dramatic shifts affect mood, energy, and tension patterns
- Breastfeeding Demands: Milk production requires both adequate rest and stress hormone management
- Sleep Disruption: Fragmented sleep creates nervous system dysregulation requiring conscious counterbalancing
- Physical Adaptation: Baby-holding positions create new tension patterns needing release
Psychological Dimensions of Postpartum Relaxation
Equally important are the mental and emotional aspects:
- Identity Transformation: Processing the shift to motherhood requires integration space
- Overwhelming Responsibility: The weight of infant dependency creates mental load needing release
- Loss of Personal Space: Constant contact with baby creates touch saturation requiring balance
- Decision Fatigue: Continuous parenting choices deplete mental resources requiring replenishment
- Anxiety Management: Natural protective instincts can escalate to overwhelming worry without regulation
Against this backdrop, effective postpartum relaxation techniques must address multiple dimensions simultaneously while fitting realistically into new motherhood’s constraints.
Key Relaxation Techniques in Postnatal Yoga
The following techniques offer particularly valuable support during the postpartum period:
1. Supported Restorative Poses for Complete Rest
These deeply restful positions require minimal muscular effort while providing maximum nervous system regulation:
a) Supported Reclining Bound Angle (Supta Baddha Konasana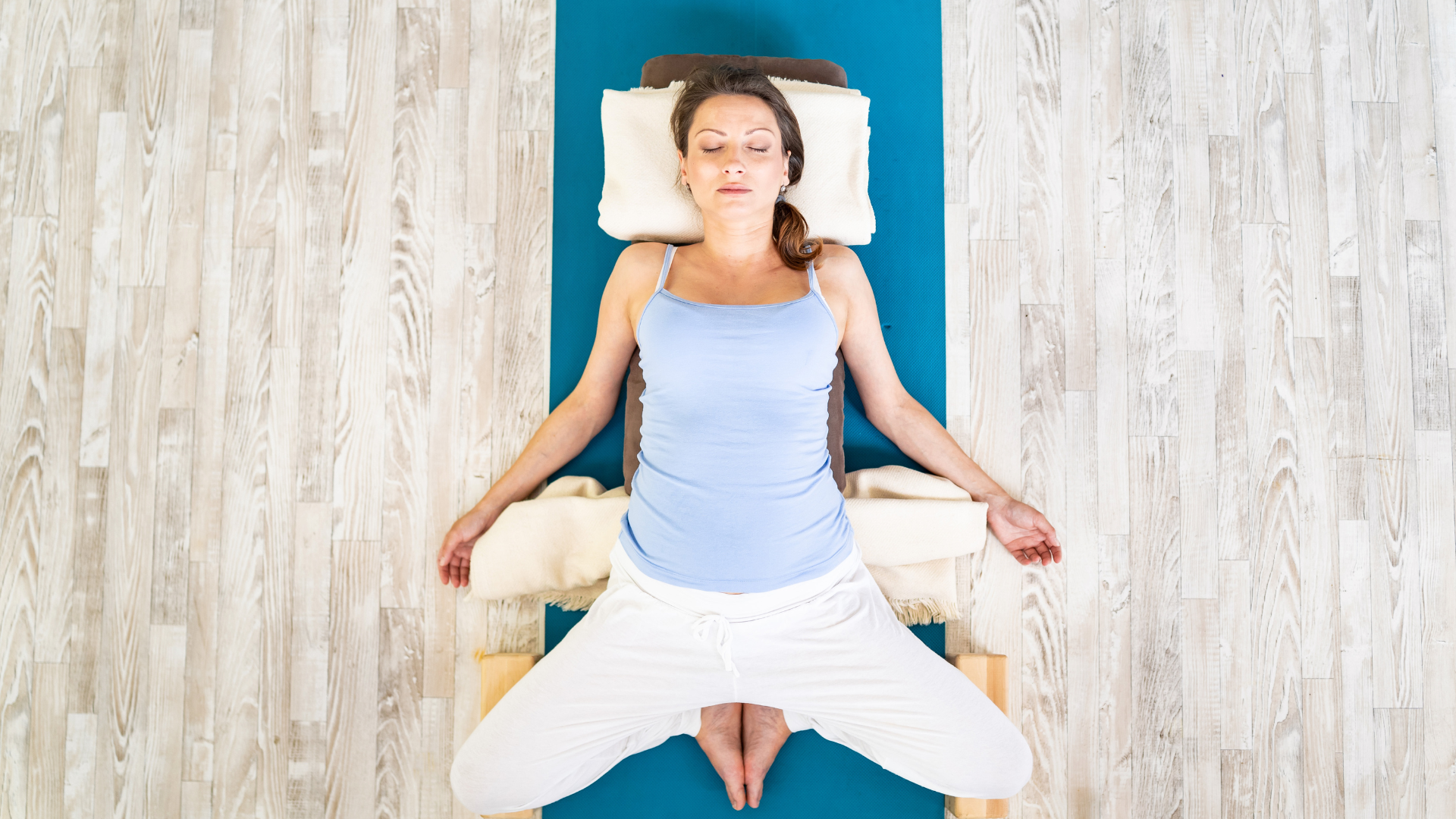 )
)
This heart-opening position counteracts nursing posture while supporting pelvic healing:
- Sit in front of a bolster or cushion stack with sacrum touching support
- Bring soles of feet together, allowing knees to fall outward
- Recline back onto support, allowing spine and head to rest completely
- Optional: add cushions under outer thighs for additional support
- Remain for 5-15 minutes, focusing on extended exhales
Benefits: Relieves upper back tension from nursing positions, improves lymphatic flow in breast tissue, addresses postpartum pelvic congestion, and triggers parasympathetic response.
b) Side-Lying Relaxation Pose
This position supports those with diastasis recti, cesarean recovery, or hemorrhoids:
- Lie on one side with support between knees and ankles
- Place a folded blanket under the waist for spinal support
- Support head with folded blanket or cushion
- Slightly bend both knees for stability
- Rest top arm on side or supported on cushion
- Remain for 5-15 minutes, then repeat on opposite side
Benefits: Avoids pressure on healing abdominal tissues, prevents sacroiliac strain, allows complete muscular surrender, and mimics a natural sleeping position enhancing relaxation response.
c) Legs-Up-the-Wall Variation (Viparita Karani)
This gentle inversion addresses postpartum circulation challenges:
- Position bolster or folded blankets 6 inches from wall
- Sit sideways on support with hip touching wall
- Swing legs up wall while lowering torso to floor
- Allow arms to rest in comfortable position
- For postpartum comfort, keep legs wider apart rather than together
- Remain for 5-10 minutes with focus on abdominal breathing
Benefits: Reduces lower extremity swelling, relieves pelvic congestion, improves circulation to healing tissues, and provides gentle stretching for lower back without effort.
2. Breath-Centered Techniques for Nervous System Regulation
These accessible practices can be implemented even during baby-care moments:
a) Extended Exhale Breathing
This simple technique activates the parasympathetic nervous system:
- Find a comfortable seated or reclined position
- Inhale normally through nose for a count of four
- Exhale slowly through slightly pursed lips for count of six or eight
- Continue for 1-3 minutes, extending exhale duration as comfortable
- Practice whenever feeling overwhelmed or before sleep attempts
Benefits: Triggers vagal tone improvement, reduces stress hormone circulation, improves sleep onset, and creates immediate calming effect accessible during parenting challenges.
b) Alternate Nostril Breathing (Nadi Shodhana)
This balancing practice helps regulate emotional fluctuations:
- Sit comfortably with spine supported
- Rest left hand on lap or holding baby
- Use right thumb to close right nostril, inhale through left
- Use right ring finger to close left nostril, exhale through right
- Inhale through right, close with thumb, exhale through left
- Continue alternating for 1-3 minutes
- Can be practiced one-handed while nursing or holding sleeping baby
Benefits: Balances sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, improves emotional stability, enhances respiratory efficiency, and provides mental focusing effect during overwhelming moments.
For ongoing wellbeing beyond the immediate postpartum period, Online Yoga Classes offer diverse approaches supporting the continued balance between activity and restoration that remains essential throughout the parenting journey.
c) Humming Bee Breath (Bhramari)
This vibration-based technique calms an agitated mind:
- Sit or recline comfortably
- Take deep inhale through nose
- With lips lightly closed, create humming sound during exhale
- Focus on feeling vibration throughout skull and chest
- Repeat 5-10 times, allowing sound to become softer
- Can be practiced quietly enough not to wake a sleeping baby
Benefits: Immediate thought-slowing effect, reduces mental chatter, creates gentle massage effect for brain, and triggers relaxation response through cranial nerve stimulation.
3. Guided Relaxation Practices for Mental Restoration
These techniques provide essential mental reset during intense postpartum periods:
a) Body Scan for Tension Release
This practice addresses unconscious tension patterns common postpartum:
- Lie or sit in comfortable, supported position
- Systematically bring attention to each body part, moving from feet to head
- Notice and consciously release any holding or tightness
- Give special attention to jaw, shoulders, and pelvic floor
- Can be practiced during baby’s nap or even while nursing
Benefits: Identifies and releases unconscious tension patterns, improves body awareness, reduces pain from holding patterns, and creates full-body relaxation response.
b) Mini Yoga Nidra for Sleep Support
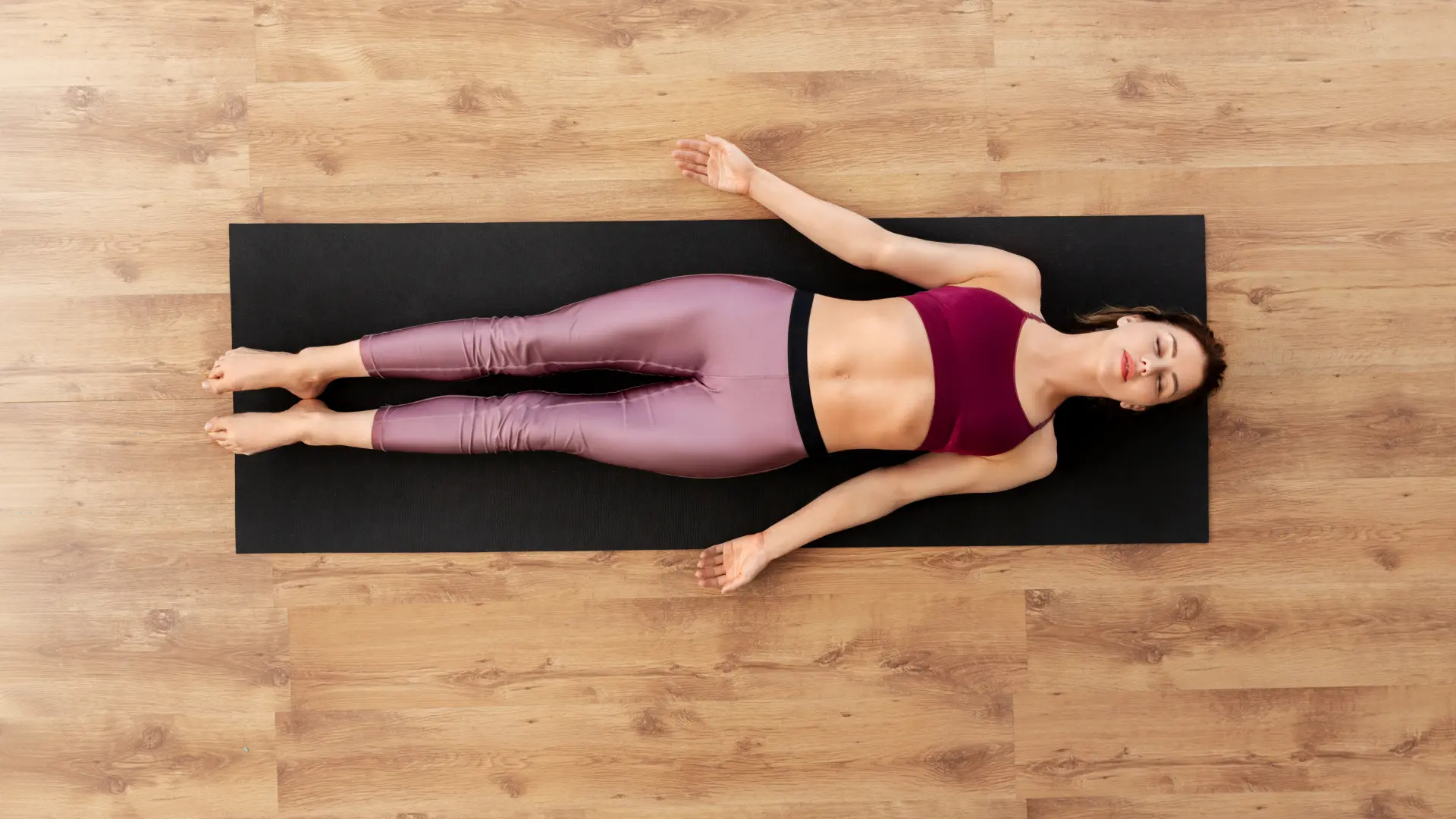

This abbreviated yogic sleep technique supports rest during limited windows:
- Lie in comfortable position with support as needed
- Follow guided awareness through body parts, breath, and sensations
- Maintain state between wakefulness and sleep
- Even 5-10 minutes provides significant restoration
- Can be practiced when baby first falls asleep to maximize rest opportunity
Benefits: Creates restoration equivalent to deeper sleep in shorter time, helps manage sleep deprivation effects, supports emotional regulation, and enhances ability to rest quickly when opportunity arises.
c) Sankalpa (Intention) Practice for Emotional Center
This intention-setting technique provides emotional anchoring:
- In relaxed state, identify a short, positive statement of intent
- Phrase in present tense as if already true (e.g., “I am resting while I can”)
- Mentally repeat statement 3-5 times during relaxed breathing
- Return to intention during challenging moments
- Update intention weekly to address current challenges
Benefits: Creates mental focal point during emotional overwhelm, replaces negative thought spirals, supports self-compassion development, and provides psychological continuity during identity transition.
4. Gentle Movement Flows for Tension Release
These minimal movement sequences release accumulated tension without requiring significant energy:
a) Wrist and Hand Release Sequence
This practice addresses tension from holding and carrying baby:
- Extend arms forward, gently flex and extend wrists
- Create circular movements in both directions
- Spread fingers wide, then make fists, repeating several times
- Interlace fingers, stretch arms forward, then overhead if comfortable
- Gently shake out any remaining tension
- Can be practiced one hand at a time while holding baby
Benefits: Relieves repetitive strain from baby carrying, improves circulation to hands and forearms, prevents carpal tunnel symptoms common in postpartum, and provides quick relief without dedicated practice time.
b) Neck and Shoulder Tension Release
This sequence addresses nursing and carrying tension patterns:
- Gently drop right ear toward right shoulder, hold 3-5 breaths
- Repeat on left side
- Roll shoulders forward 5 times, then backward 5 times
- Interlace hands behind back, gently open chest if comfortable
- Draw gentle circles with nose to release neck tension
- Can be integrated into daily activities or nursing sessions
Benefits: Counters forward-head posture from infant care, relieves upper trapezius tension, improves circulation to neck and shoulders, and prevents tension headaches common postpartum.
c) Supported Backbending Sequence
This gentle sequence counteracts rounded posture from baby care:
- Stand facing wall, arms overhead, hands on wall
- Walk feet back slightly, creating gentle upper back extension
- For supported bridge: lie with feet flat, lift hips, place block under sacrum
- For supported fish: place block or rolled towel under mid-back while reclined
- Hold each position 5-10 breaths, focusing on chest expansion
Benefits: Counteracts postural patterns from nursing and baby-carrying, opens chest for deeper breathing, relieves mid-back tension, and provides emotional lifting effect through heart opening.
Creating Realistic Postpartum Relaxation Practice
For new mothers, implementation matters as much as technique:
Integration into Baby Care Rhythm
Rather than requiring separate practice time:
- Practice extended exhales during nighttime feedings
- Incorporate gentle neck stretches while nursing
- Use legs-up-the-wall pose while baby plays nearby
- Practice body scan while lying next to sleeping baby
- Create “relaxation stations” in baby care areas with needed props
Micro-Practice Development
Breaking techniques into minimal effective doses:
- Identify 1-2 minute variations of techniques
- Practice brief relaxation triggers throughout day
- Look for natural pauses in baby care for quick resets
- Recognize that consistency trumps duration
- Create “relaxation anchors” that can be accessed instantly
Preparation for Limited Opportunities
Setting the stage for immediate practice:
- Keep props organized and accessible in multiple locations
- Create simple written reminders of key techniques
- Prepare guided relaxation recordings of various lengths
- Establish “nap priorities” list for self-care during baby sleep
- Identify minimal environmental needs for effective relaxation
Expert Guidance for Postnatal Relaxation

While self-directed practice offers benefits, specialized instruction ensures techniques specifically adapted to postpartum needs.
Dedicated Online Post Natal Yoga Classes provide structured approaches addressing the unique relaxation needs of new mothers, with appropriate modifications for various birth recoveries and postpartum stages.
Beyond Physical Techniques: The Psychology of Postpartum Rest
Perhaps the most essential aspect of postpartum relaxation involves addressing the mental barriers to rest:
Permission Framework Development
Many mothers struggle with allowing themselves to rest:
- Recognize rest as essential recovery, not luxury
- Understand relaxation as supporting, not competing with, baby care
- Identify and challenge “productivity programming” about constant activity
- Reframe relaxation as modeling healthy self-care for children
- Develop self-compassion language countering internal criticism about resting
Expectation Management
Realistic expectations support effective relaxation:
- Acknowledge the profound difference between pre-baby and postpartum rest
- Embrace the value of micro-relaxation rather than extended practice
- Recognize fluctuating practice needs through different postpartum phases
- Allow techniques to adapt to changing baby schedules and developmental stages
- Celebrate small moments of successful rest rather than focusing on limitations
By approaching postnatal relaxation through this specialized framework—addressing the unique physical, hormonal, emotional, and practical constraints of new motherhood—women can discover techniques that provide essential restoration within the beautiful chaos of early parenting, supporting their wellbeing and their capacity to fully embrace this transformative life chapter
Inquiry
If you have any questions, please feel free to reach out. We’ll be glad to help!